Use of Fuel Outside ISO 4406 Standards
Fuel is a critical component in numerous industrial sectors, including transportation and power generation. Its quality is essential not only for the optimal performance of equipment but also for minimizing environmental impact. ISO 4406 sets the acceptable levels of particulate contamination in fluids, which engine manufacturers use to determine the maximum and optimal limits that fuel must meet to ensure peak equipment performance. However, using fuel that does not comply with this standard can have significant environmental consequences.
1
Pollutant
Emissions
2
Damage to
Biodiversity
3
Impact on Human Health
4
Increase in Waste and Wastefulness
1
Pollutant
Emissions
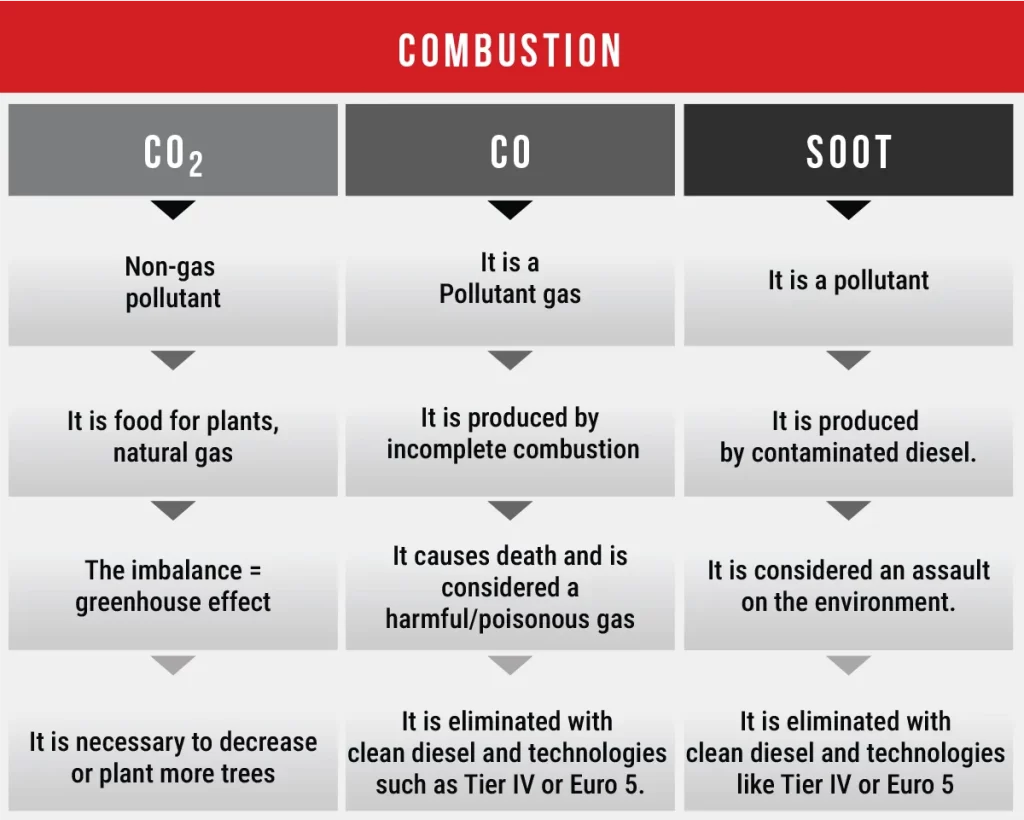
Fuel that does not meet the ISO 4406 standards may contain high levels of impurities, which in turn lead to the emission of various gases and particles. Among these gases are carbon dioxide (CO₂)—a naturally occurring gas that is not inherently polluting—and carbon monoxide (CO), a highly toxic and harmful pollutant. In addition, particulate matter (PM), along with other contaminants, contributes to the imbalance of CO₂ in the atmosphere, potentially worsening global warming and the greenhouse effect.
Reducing the levels of impurities in fuel—such as water and suspended particles (as reflected in the ISO classification)—helps lower harmful emissions. This not only decreases the concentration of CO₂ but also reduces other harmful gases, including sulfur dioxide (SO₂) and nitrogen oxides (NOx). Lowering these emissions is essential to mitigating secondary environmental effects such as acid rain and global warming, which negatively impact air quality, public health, and the climate.
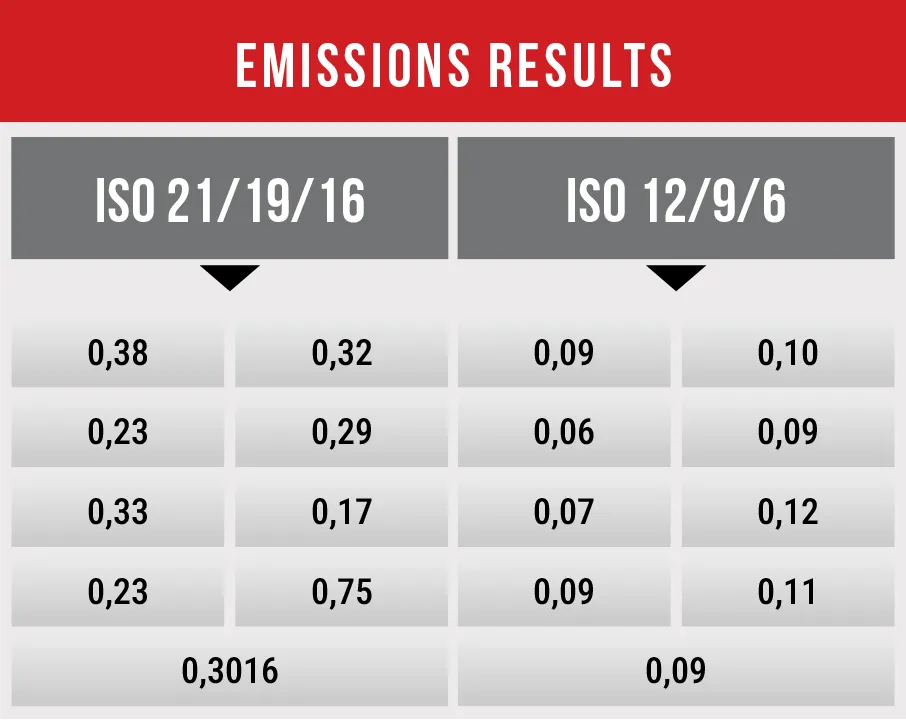
In a study conducted by Dr. Edwin Ramírez, a researcher at the National Institute of Learning (INA) in Costa Rica, four truck engines were evaluated at different times. The objective was to compare the levels of environmental pollution emitted when using fuel with impurity levels above the maximum recommended by engine manufacturers versus using fuel within the optimal specified range. The results revealed significant differences in emission levels.
2
Damage to
Biodiversity
Emissions resulting from the use of low-quality fuel can have adverse effects on natural ecosystems, impacting the health of local flora and fauna.
Pollutants can accumulate in soil and water bodies, compromising biodiversity and threatening the health of both aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems.

3
Impact on
Human Health
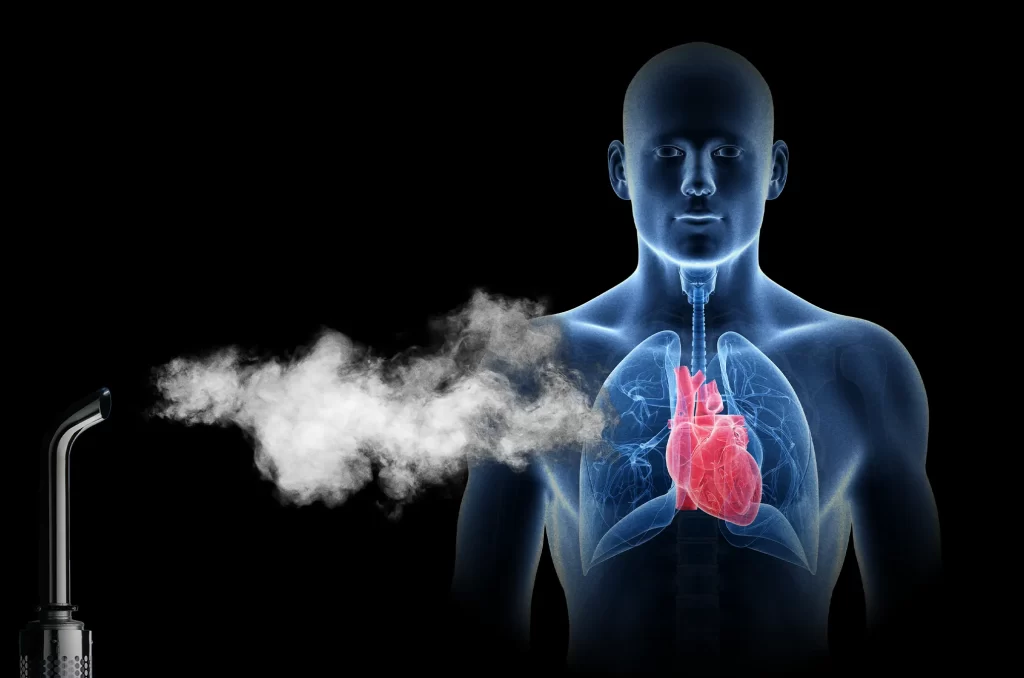
Exposure to pollutants emitted from the use of fuel that does not comply with the tolerance levels recommended by engine manufacturers, based on ISO 4406 standards, can have serious consequences for human health.
Fine particles and harmful chemical compounds present in these emissions can lead to respiratory and cardiovascular issues, among other adverse health effects—particularly in vulnerable populations such as children, the elderly, and individuals with pre-existing respiratory conditions.
4
Increase in Waste
and Wastefulness
Off-spec fuel can produce greater amounts of waste during both processing and combustion.
This not only increases the need for waste treatment and disposal but also contributes to the generation of waste materials that can pollute the environment if not properly managed.

Conclusion
The use of fuel that does not meet the cleanliness levels recommended by manufacturers within the ISO 4406 standard has multiple adverse environmental impacts, ranging from air and water pollution to harm to human health and biodiversity. It is essential that OEMs, regulatory authorities, and end-users work together to ensure compliance with fuel quality standards, thereby promoting sustainable development and protecting the environment for future generations.



